패턴명칭
Memento
필요한 상황
시간에 따른 순차적인 연산을 수행하면서, 원하는 시점의 상태로 되돌아갈 필요가 있을때 사용하는 패턴이다.
예제 코드
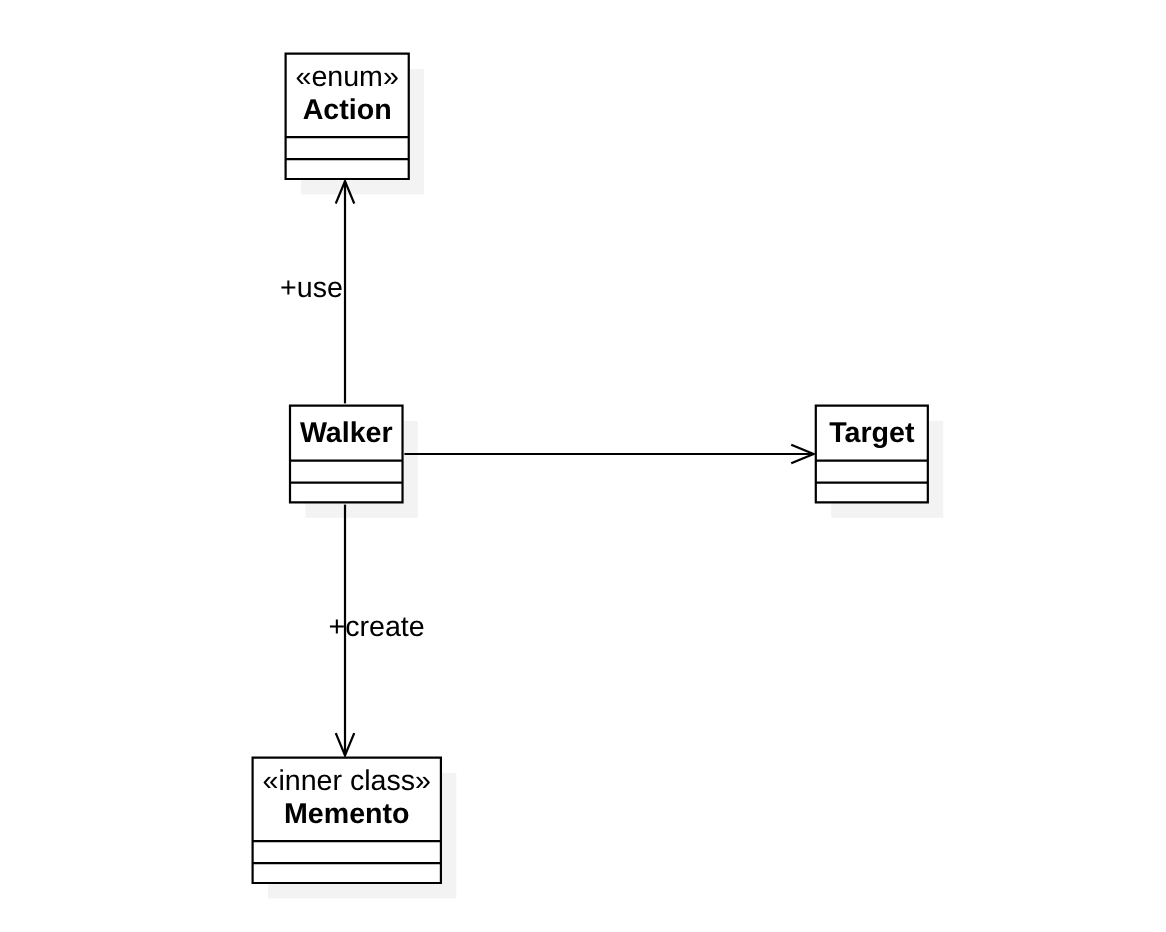
Walker 클래스의 객체는 위, 오른쪽, 아래, 왼쪽으로 1 단위씩 이동하여 점점 Target 클래스의 객체에 저장된 x, y 좌표로 가도록 가장 최적의 Walker 객체의 상태를 Memento 클래스를 이용해 저장하고 다시 복원한다. Memento 클래스는 Walker의 inner class인데, 이유는 오직 Walker에만 정보를 전달하기 위함이다. 동시에 Memento의 생성자는 private인데 이는 오직 Walker만이 Memento 객체를 생성할 수 있도록 하기 위함이다. 먼저 Target 클래스이다.
package tstThread;
public class Target {
private int x;
private int y;
public Target(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getDictance(int x0, int y0) {
return Math.sqrt((x-x0)*(x-x0)+(y-y0)*(y-y0));
}
}
다음은 Action 열거자이다.
package tstThread;
public enum Action {
UP, RIGHT, DOWN, LEFT;
public static Action fromIndex(int i) {
if(i == 0) return UP;
else if(i == 1) return RIGHT;
else if(i == 2) return DOWN;
else return LEFT;
}
}
다음은 Walker 클래스와 그 내부 클래스인 Memento 클래스이다.
package tstThread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Walker {
private int x;
private int y;
private ArrayList<Action> actions = new ArrayList<Action>();
public Walker(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double walk(Action action, Target target) {
actions.add(action);
if(action == Action.UP) {
y += 1;
} else if(action == Action.RIGHT) {
x += 1;
} else if(action == Action.DOWN) {
y -= 1;
} else if(action == Action.LEFT) {
x -= 1;
}
return target.getDictance(x, y);
}
public class Memento {
private int x;
private int y;
private ArrayList<Action< actions;
private Memento() {}
}
public Memento createMemento() {
Memento memento = new Memento();
memento.x = this.x;
memento.y = this.y;
memento.actions = (ArrayList<Action>)this.actions.clone();
return memento;
}
public void restoreMemento(Memento memento) {
this.x = memento.x;
this.y = memento.y;
this.actions = (ArrayList<Action>)memento.actions.clone();
}
public String toString() {
return actions.toString();
}
}
끝으로 지금까지의 클래스들을 사용하는 코드이다.
package tstThread;
import java.util.Random;
import tstThread.Walker.Memento;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Target target = new Target(10, 10);
Walker walker = new Walker(0, 0);
Random random = new Random();
double minDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
Memento memento = null;
while(true) {
Action nextAction = Action.fromIndex(random.nextInt(4));
double distance = walker.walk(nextAction, target);
System.out.println(nextAction + " " + distance);
if(distance == 0.0) {
break;
}
if(minDistance > distance) {
minDistance = distance;
memento = walker.createMemento();
} else {
if(memento != null) {
walker.restoreMemento(memento);
}
}
}
System.out.println("Walker's path: " + walker);
}
}
실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
RIGHT 13.45362404707371 LEFT 14.142135623730951 RIGHT 12.806248474865697 DOWN 13.601470508735444 UP 12.041594578792296 UP 11.313708498984761 DOWN 12.041594578792296 DOWN 12.041594578792296 DOWN 12.041594578792296 RIGHT 10.63014581273465 RIGHT 10.0 UP 9.219544457292887 LEFT 9.899494936611665 RIGHT 8.602325267042627 LEFT 9.219544457292887 LEFT 9.219544457292887 LEFT 9.219544457292887 LEFT 9.219544457292887 UP 7.810249675906654 LEFT 8.48528137423857 RIGHT 7.211102550927978 DOWN 8.06225774829855 UP 6.4031242374328485 DOWN 7.211102550927978 RIGHT 5.830951894845301 DOWN 6.708203932499369 DOWN 6.708203932499369 UP 5.0 DOWN 5.830951894845301 DOWN 5.830951894845301 RIGHT 4.47213595499958 DOWN 5.385164807134504 RIGHT 4.123105625617661 DOWN 5.0990195135927845 RIGHT 4.0 LEFT 4.123105625617661 DOWN 5.0 DOWN 5.0 RIGHT 4.123105625617661 UP 3.0 UP 2.0 LEFT 2.23606797749979 UP 1.0 LEFT 1.4142135623730951 LEFT 1.4142135623730951 DOWN 2.0 UP 0.0 Walker's path: [RIGHT, RIGHT, UP, UP, RIGHT, RIGHT, UP, RIGHT, UP, RIGHT, UP, RIGHT, UP, RIGHT, RIGHT, RIGHT, UP, UP, UP, UP]
Walker 객체가 어떤 행위를 취했을때 이전의 행위에 대한 목적지까지의 거리보다 더 멀어지면, 이전의 상태로 돌아가기 위해 Memento 객체를 사용하고 있다.
이 글은 소프트웨어 설계의 기반이 되는 GoF의 디자인패턴에 대한 강의자료입니다. 완전한 실습을 위해 이 글에서 소개하는 클래스 다이어그램과 예제 코드는 완전하게 실행되도록 제공되지만, 상대적으로 예제 코드와 관련된 설명이 함축적으로 제공되고 있습니다. 이 글에 대해 궁금한 점이 있으면 댓글을 통해 남겨주시기 바랍니다.
