원문은 https://opencv-python-tutroals.readthedocs.io/en/latest/py_tutorials/py_gui/py_image_display/py_image_display.html#display-image 입니다.
OpenCV는 단일 이미지나 동영상의 이미지를 원하는 결과를 분석 및 추출하기 위한 API입니다. OpenCV는 C/C++ 언어로 개발되었고, 이 API를 사용할 수 있는 언어는 C/C++, Java, Python 등입니다. 그리고 활용할 수 있는 플랫폼은 Windows, Linix, Android, iOS 등입니다. 이 글은 OpenCV를 Python 언어를 이용해 학습하면서 정리할 필요가 있다고 판단되는 핵심내용을 꼼꼼이 기록하기 위한 목적을 갖습니다. 각 글에 대한 원문은 글의 서문에 언급해 두고 있으니, 참고하시기 바랍니다. 아울리 이 글은 필자가 원문의 내용을 통해 학습하고 필자 나름대로 재해석하여 글을 작성하고 있습니다. 이 글과 이후의 Python과 OpenCV 관련글은 모두 이와 같습니다.
OpenCV와 Python의 설치 방법은 생략합니다. 검색을 통해 각자 자신에 맞는 환경에 설치하기 바랍니다.
OpenCV는 이미지를 대상으로 어떤 처리를 수행하므로 이미지를 읽고 화면에 표시하는 것은 매우 중요하고 기초적인 내용입니다. 이 글은 바로 이미지를 읽어 화면에 표시하는 내용에 대한 글입니다. 가장 먼저 작성된 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
import numpy as np
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('./data/quark-particle-flavors.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
k = cv2.waitKey()
if k == ord('s'):
cv2.imwrite('d:/z.jpg', img)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
1,2번 코드는 OpenCV API 사용을 위한 모듈을 불러들이는 코드입니다. OpenCV는 이미지 데이터를 numpy의 자료구조를 사용합니다. 그러므로 OpenCV의 사용에 있어 numpy 모듈은 항상 함께 합니다.
실제 이미지를 불러 들이는 코드는 4번의 cv2.imread 함수인데, 첫번째 인자는 불러드릴 이미지 파일명이며 두번째는 해당 이미지를 불러와 어떤 포맷으로 메모리에 적재해 numpy 자료 구조의 객체를 생성할 것인지입니다. 위의 코드에서는 cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE로써 비록 해당 원본 이미지가 RGB의 칼라 이미지이지만 Gray 색상으로 해석해 이미지 객체를 반환하라는 것입니다. cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE 이외에도 사용할 수 있는 값은 다음과 같습니다.
- cv2.IMREAD_COLOR : 별도로 지정하지 않을 경우 사용되는 기본값이며 칼라 이미지로 읽어드림. 이미지의 투명도값은 무시된다.
- cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE : 이미지를 Grayscale로 읽는다
- cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED : 투명도인 Alpha 채널을 포함하여 읽는다.
반환된 이미지는 img 변수에 담기며 img 변수의 type을 확인해 보면 ‘numpy.ndarray’라는 타입으로 표시됩니다. 이제 이 이미지를 표시하기 위해 6번의 코드인 cv2.imshow 함수가 사용되는데 첫번째 인수는 이미지가 표시되는 Window의 식별자인 이름이고 두번째가 표시되는 이미지 객체입니다. 표시되는 이미지 객체는 4번 코드에서 정의된 변수입니다.
8번 코드는 사용자가 키 입력을 기다리는 함수인 cv2.waitKey로 인자값이 없거나 0일 경우 시간 제한없이 사용자의 키 입력을 기다립니다. 인자가 지정되면 해당값의 시간만큼만 키 입력을 기다립니다.>/p>
10번 코드는 입력된 키값이 소문자 s일 경우 img 객체의 저장된 이미지를 또 다른 파일로 저장하라는 cv2.imwrite 함수입니다.
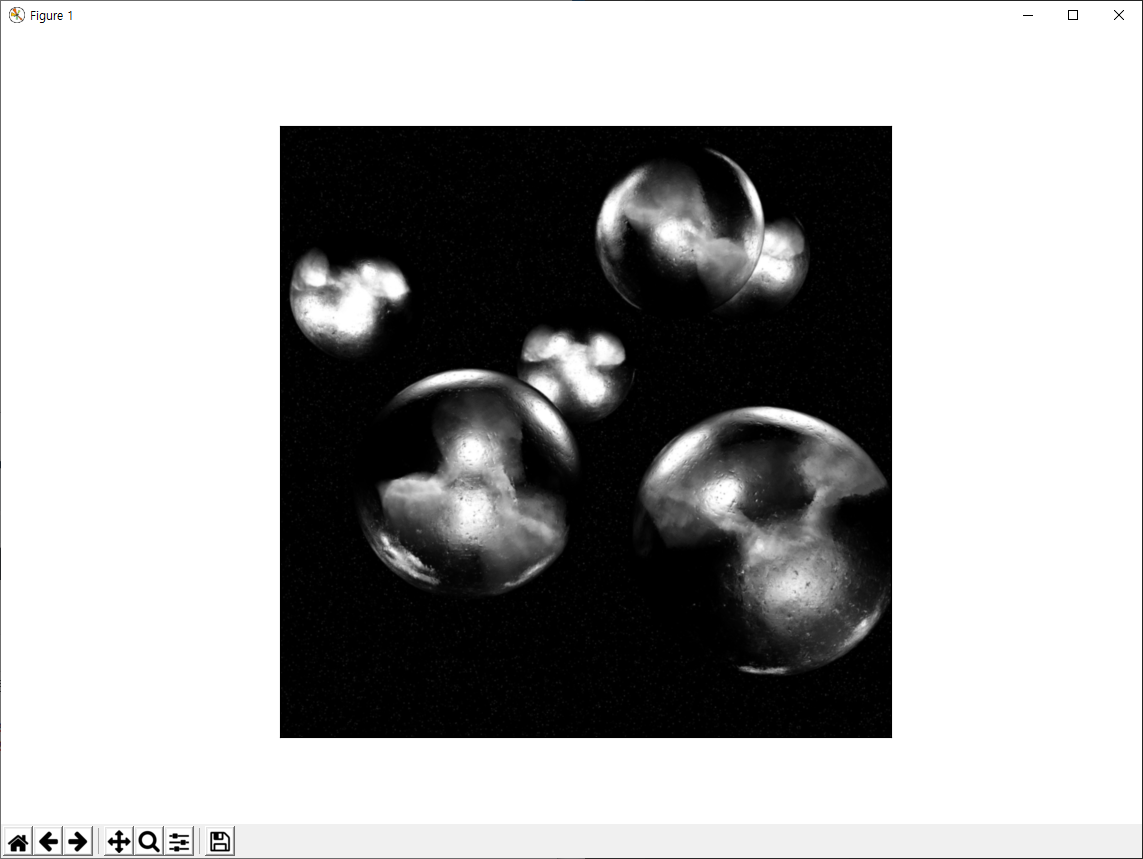
13번은 프로그램의 종료를 위해 표시된 모든 Window을 닫으라는 코드입니다. 실행해보면 다음 화면과 같습니다.
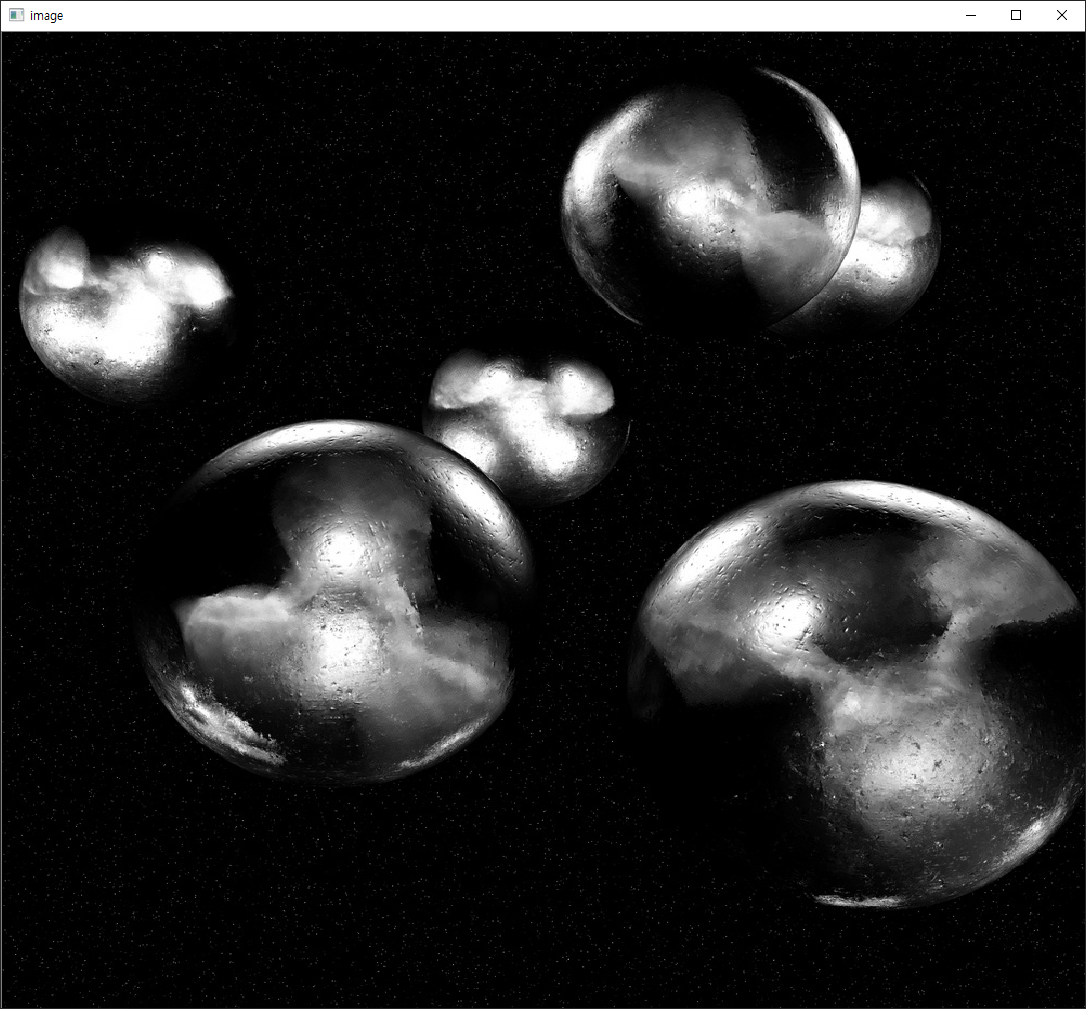
이미지의 표시는 OpenCV 방식만 있는것이라 아니고 Matplotlib를 사용할 수도 있습니다. 이미지 처리의 결과를 그래프를 통해 효과적으로 표시하기 위해 Matplotlib를 사용합니다. Matplotlib를 이용한 이미지 표시의 코드는 아래와 같습니다.
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('./data/quark-particle-flavors.jpg', 0)
plt.imshow(img, cmap = 'gray', interpolation = 'bicubic')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
실행 결과는 다음과 같습니다.