이 글의 예제 코드는 THREE.JS 공식 사이트의 EXAMPLES에서 제공되는 코드를 이해하고 제 나름대로의 코드로 재구성한 것입니다.
fetch API를 이용한 REST API 호출
2개 REST API를 순차적으로 호출하는 코드는 아래와 같습니다.
const url1 = "http://localhost:8080/Xr?qryHub|0004259886";
const url2 = "http://localhost:8080/Xr?qryHub|0002097186";
fetch(url1).then(response => {
return response.json();
}).then(json => {
console.log("First", json);
return fetch(url2);
}).then(response => {
return response.json();
}).then(json => {
console.log("Second", json);
}).catch(function (error) {
console.warn(error);
});
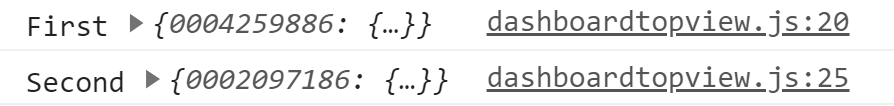
url1에 대한 REST API의 호출이 성공하면 url2에 대한 REST API가 호출됩니다. 이 두 개의 REST API가 문제가 없다면 결과가 호출된 순서대로 아래처럼 콘솔에 표시됩니다.
위의 코드를 보면 2개의 REST API는 그 결과에 종속적이지 않으므로 순차적으로 호출하지 않고 동시에 호출하는 것이 효율적입니다. 아래의 코드는 이 2개의 REST API를 동시에 호출하여 2개의 결과를 취합해 출력하는 코드입니다.
const url1 = "http://localhost:8080/Xr?qryHub|0004259886";
const url2 = "http://localhost:8080/Xr?qryHub|0002097186";
Promise.all([fetch(url1), fetch(url2)]).then(responses => {
return Promise.all(responses.map(response => {
return response.json();
}));
}).then(json => {
console.log(json);
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error);
});
결과는 다음과 같습니다.

지금까지 살펴보면 REST API는 GET 방식인데요. POST 방식을 fetch API로 호출하는 코드의 예는 다음과 같습니다.
const url = "http://localhost:8080/Xr?sql|postgis|1";
fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
//headers: { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain;charset=UTF-8' },
body: `
SELECT 0 as project_id, zone_id, hub_id
FROM zone_hub_map
WHERE zone_id
IN (
SELECT zone_id FROM project_zone_map WHERE project_id = 0
);
`
}).then(response => {
return response.text();
}).then(text => {
console.log(text);
});
결과는 다음과 같습니다.


