옛다.
npm install -g http-server
홈 디렉토리로 이동해서 아래처럼 실행하면 끝!
http-server -p 8080

공간정보시스템 / 3차원 시각화 / 딥러닝 기반 기술 연구소 @지오서비스(GEOSERVICE)
옛다.
npm install -g http-server
홈 디렉토리로 이동해서 아래처럼 실행하면 끝!
http-server -p 8080

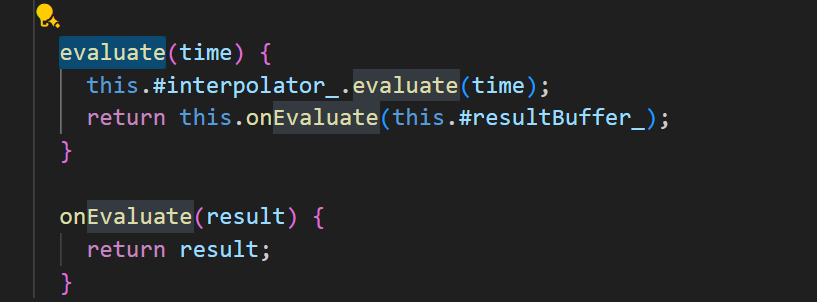
반환 타입을 내 입맛대로 변경할 수 있는 묘수의 코드. 됐어! 이제! 역시 이미지 생성은 ChatGPT가 갑인데….
const user = { name: 'Alice', age: 30, city: 'Seoul' };
// 객체 구조 분해
const { name, age } = user;
console.log(name, age); // Alice 30
const { name: name2, ...sss } = user;
console.log(name2, sss); // Alice { age: 30, city: 'Seoul' }
// 다른 이름으로 할당하거나 기본값 설정도 가능
const { name: fullName, email = 'noemail@example.com' } = user;
console.log(fullName, email); // Alice noemail@example.com
// 배열 구조 분해
const colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue'];
const [first, second, third] = colors;
console.log(first, second, third); // red green blue
// 일부만 추출하거나 나머지 요소들을 배열로 받을 수도 있음
const [one, two, ...rest] = colors;
console.log(one, two, rest); // red green ['blue']
/* 배열 결합 및 복사에서의 예 */
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
const arr2 = [4, 5, 6];
// 배열 결합
const combinedArr = [...arr1, ...arr2];
console.log(combinedArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
// 배열 복사 (얕은 복사)
const copiedArr = [...arr1];
console.log(copiedArr); // [1, 2, 3]
/* 객체 병합 및 복사에서의 예 */
const obj1 = { a: 1, b: 2 };
const obj2 = { c: 3, d: 4 };
// 객체 병합
const combinedObj = { ...obj1, ...obj2 };
console.log(combinedObj); // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d: 4 }
// 객체 복사 (얕은 복사)
const copiedObj = { ...obj1 };
console.log(copiedObj); // { a: 1, b: 2 }
/* 함수 인자 전달에서의 예 */
function sum(a, b, c) {
return a + b + c;
}
const numbers = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(sum(...numbers)); // 6 (배열 요소를 개별 인자로 펼쳐서 전달)
const user = {
name: 'Dave',
address: {
street: '123 Main St',
city: 'Busan'
},
// phone: '010-1234-5678' // phone 속성이 없을 수 있음
};
// 기존 방식 (에러 방지)
let city = user.address && user.address.city;
console.log(city); // Busan
let zipCode;
if (user.address && user.address.zipCode) {
zipCode = user.address.zipCode;
}
console.log(zipCode); // undefined
// 선택적 체이닝
const userCity = user.address?.city;
console.log(userCity); // Busan
const userPhone = user.phone?.number; // user.phone이 undefined이므로 userPhone은 undefined
console.log(userPhone); // undefined
const userStreet = user.address?.street;
console.log(userStreet); // 123 Main St
// 배열 요소에도 적용 가능
const arr = [{ value: 10 }];
const firstValue = arr?.[0]?.value;
console.log(firstValue); // 10
const emptyArr = [];
const nonExistentValue = emptyArr?.[0]?.value;
console.log(nonExistentValue); // undefined
const userInput = null; const defaultValue = 'default value'; // || 연산자 (Falsy 값도 걸러냄) const resultOr = userInput || defaultValue; console.log(resultOr); // default value const zeroValue = 0; const resultOrZero = zeroValue || defaultValue; console.log(resultOrZero); // default value (0도 Falsy로 간주하여 default value가 할당됨) // ?? 연산자 (null 또는 undefined만 걸러냄) const resultNullish = userInput ?? defaultValue; console.log(resultNullish); // default value const zeroValueNullish = 0; const resultNullishZero = zeroValueNullish ?? defaultValue; console.log(resultNullishZero); // 0 (0은 유효한 값으로 간주됨) const emptyString = ''; const resultNullishEmptyString = emptyString ?? defaultValue; console.log(resultNullishEmptyString); // ''
이외에도 화살표 함수, 템플릿 리터럴, 클래스, 모듈, async/await 등이 있음.
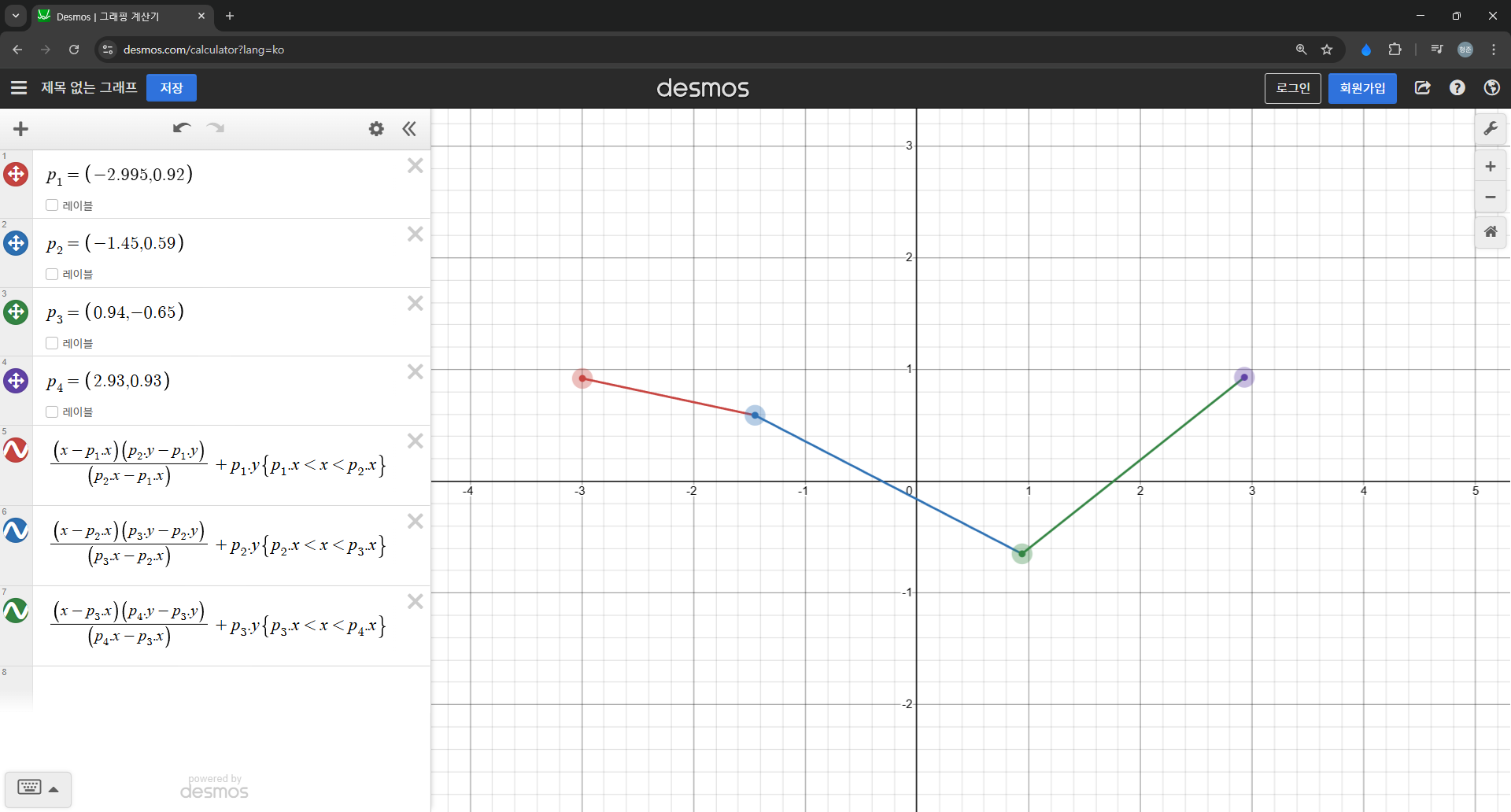
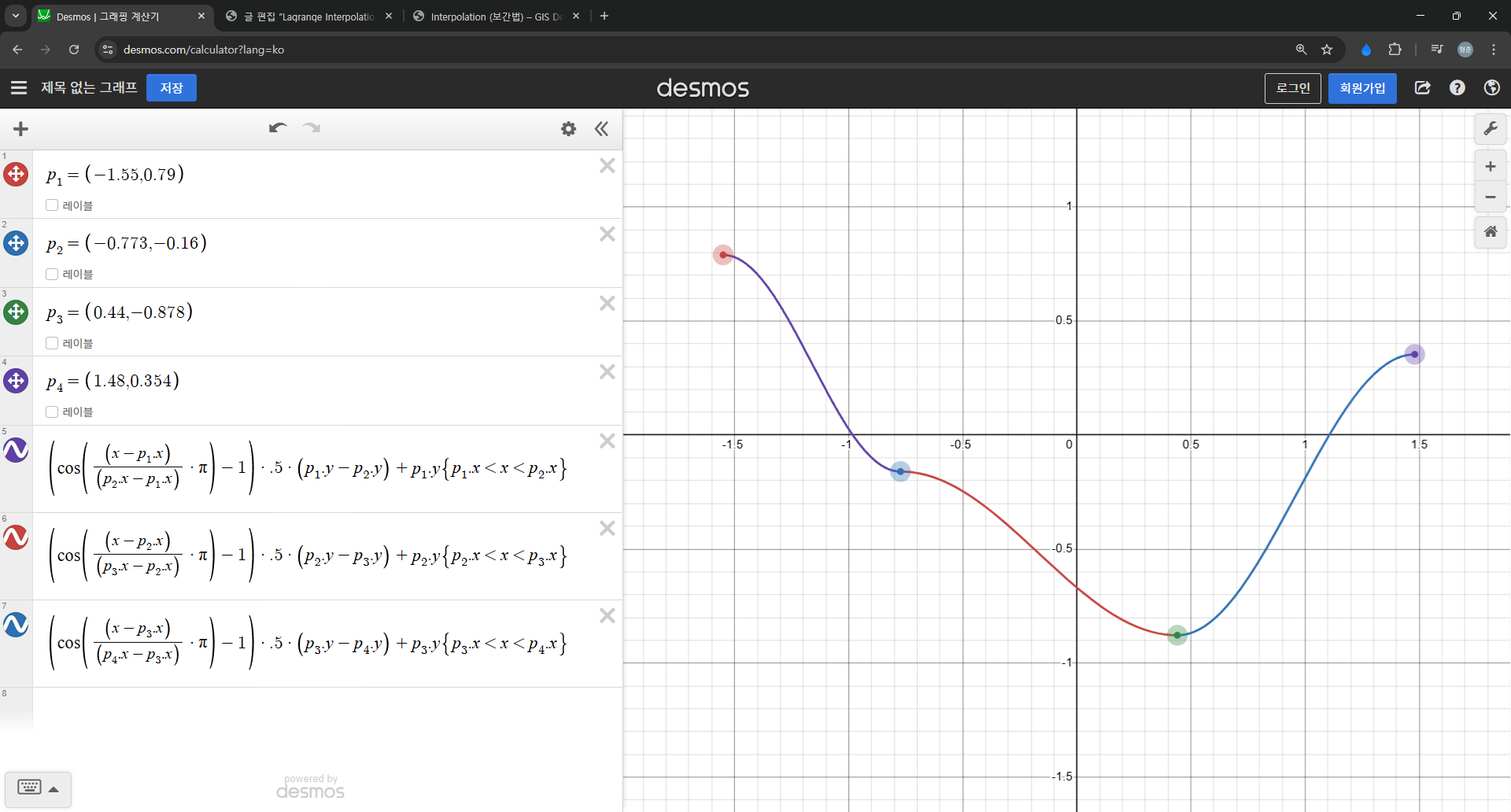
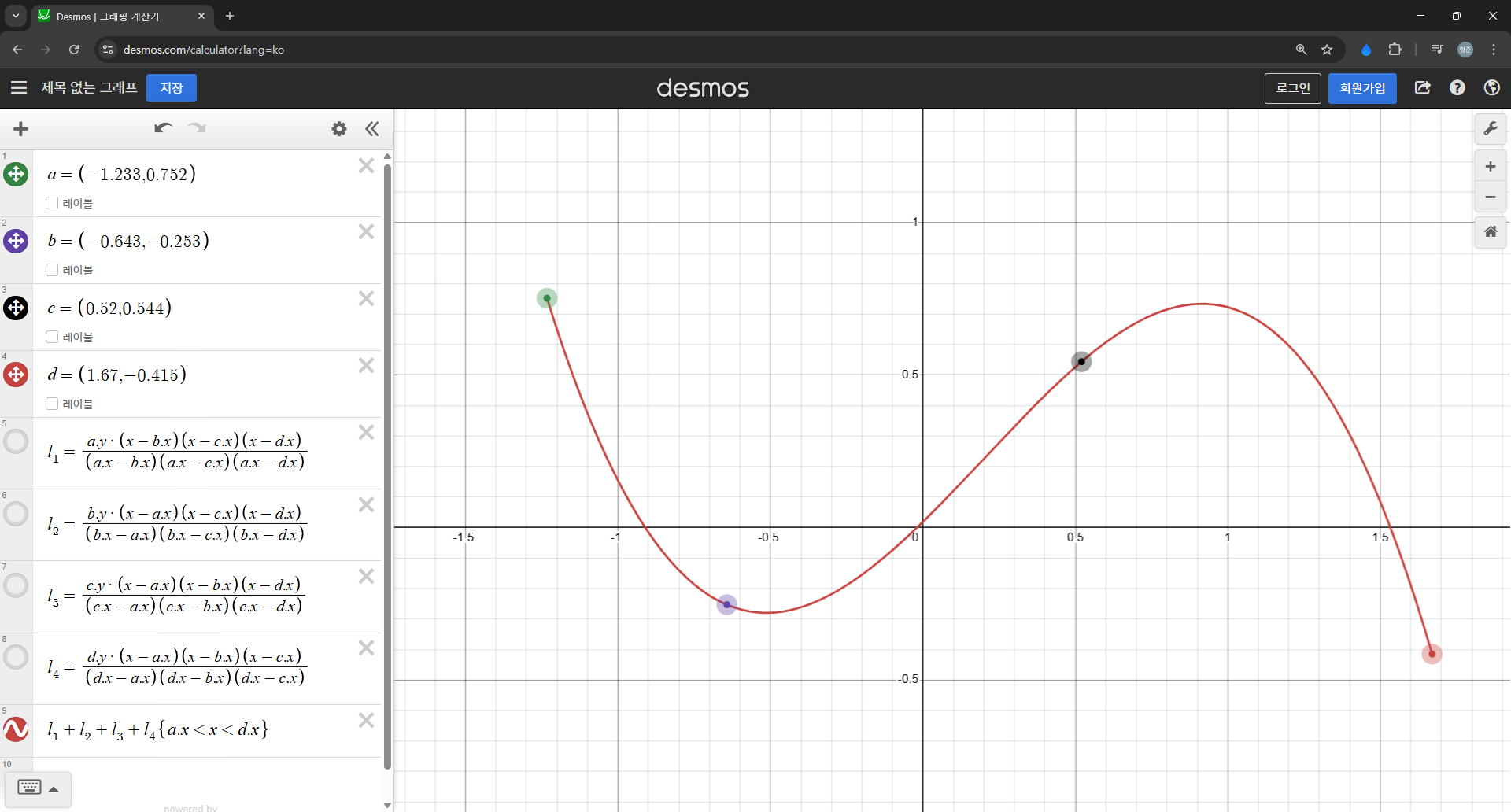
DOM 구성은 다음과 같다.
CSS는 다음과 같다.
body {
background: #bdcddb;
}
.loader {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
.circle {
position: absolute;
inset: 35px;
background-color: #acbaca;
border-radius: 50%;
box-shadow: 5px 5px 15px 0 #152b4a66,
inset 5px 5px 5px rgba(255,255,255,0.55),
-6px -6px 10px rgba(255,255,255,1);
}
.circle::before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
inset: 4px;
background: linear-gradient(#2196f3, #e91e63);
border-radius: 50%;
animation: animate 2s linear infinite;
}
@keyframes animate {
0% {
transform: rotate(0deg);
}
100% {
transform: rotate(350deg);
}
}
.circle::after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
inset: 35px;
background: #acbaca;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.circle span {
position: absolute;
inset: 4px;
background: linear-gradient(#2196f3, #e91e63);
border-radius: 50%;
animation: animate 2s linear infinite;
filter: blur(20px);
z-index: 1000;
/* mix-blend-mode: color-dodge; */
mix-blend-mode: plus-lighter;
}
.circle span::before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
inset: 40px;
background: #bdcbdb;
border-radius: 50%;
animation: animate 2s linear infinite;
z-index: 1000;
}
결과는 다음과 같다.

CSS의 67번째 줄이 핵심인데, 만약 해당 코드를 제거하면 결과는 다음과 같다.

mix-blend-mode의 값인 plus-lighter는 아직 공식적으로 문서화가 되지 않았고 만약 작동하지 않는다면 color-dodge를 사용하기 바란다. 참고로 color-dodge보다 plus-lighter가 광원의 표현에 더욱 적합하다.